#1.可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序
print('{0},{1}'.format('chuhao', 20))
print('{},{}'.format('chuhao', 20))
print('{1},{0},{1}'.format('chuhao', 20))
#2.可以设置参数
print('{name},{age}'.format(age=18, name='chuhao'))
#3.可以向str.format()传入对象:
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __str__(self):
return 'This guy is {self.name},is {self.age} old'.format(self=self)
print(str(Person('chuhao', 18)))
#4.通过映射 list
a_list = ['chuhao', 20, 'china']
print('my name is {0[0]},from {0[2]},age is {0[1]}'.format(a_list))
#5.通过映射 dict
b_dict = {'name': 'chuhao', 'age': 20, 'province': 'shanxi'}
print('my name is {name},age is {age},from {province}'.format(**b_dict))
#6.填充与对齐
print('{:>8}'.format('189'))
print('{:0>8}'.format('189'))
print('{:a>8}'.format('189'))
#7.精度与类型f,保留两位小数
print('{:.2f}'.format(321.33345))
#8.用来做金额的千位分隔符
print('{:,}'.format(1234567890))
#9.其他类型 主要就是进制了,b、d、o、x分别是二进制、十进制、八进制、十六进制。
print('{:b}'.format(18)) #二进制 10010
print('{:d}'.format(18)) #十进制 18
print('{:o}'.format(18)) #八进制 22
print('{:x}'.format(18)) #十六进制12
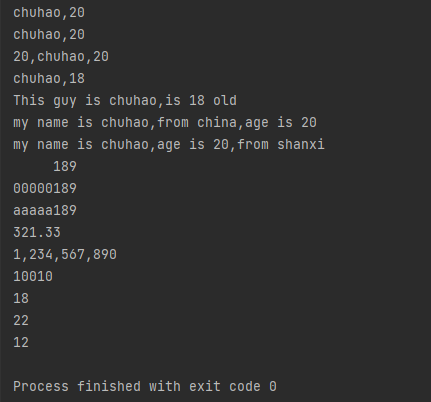
运行结果如下图: